Generating Code Coverage Metrics

 Cloud Server v3.x Server v2.x
Cloud Server v3.x Server v2.x Code Coverage tells you how much of your application is tested.
CircleCI provides a number of different options for code coverage reporting, using built-in CircleCI features combined with open source libraries, or using partners.
Viewing Coverage on CircleCI
You can upload your code coverage reports directly to CircleCI. First, add a coverage library to your project and configure your build to write the coverage report to CircleCI’s artifacts directory. Code coverage reports will then be stored as build artifacts, from where they can be viewed or downloaded. See our build artifacts guide for more on accessing coverage reports.
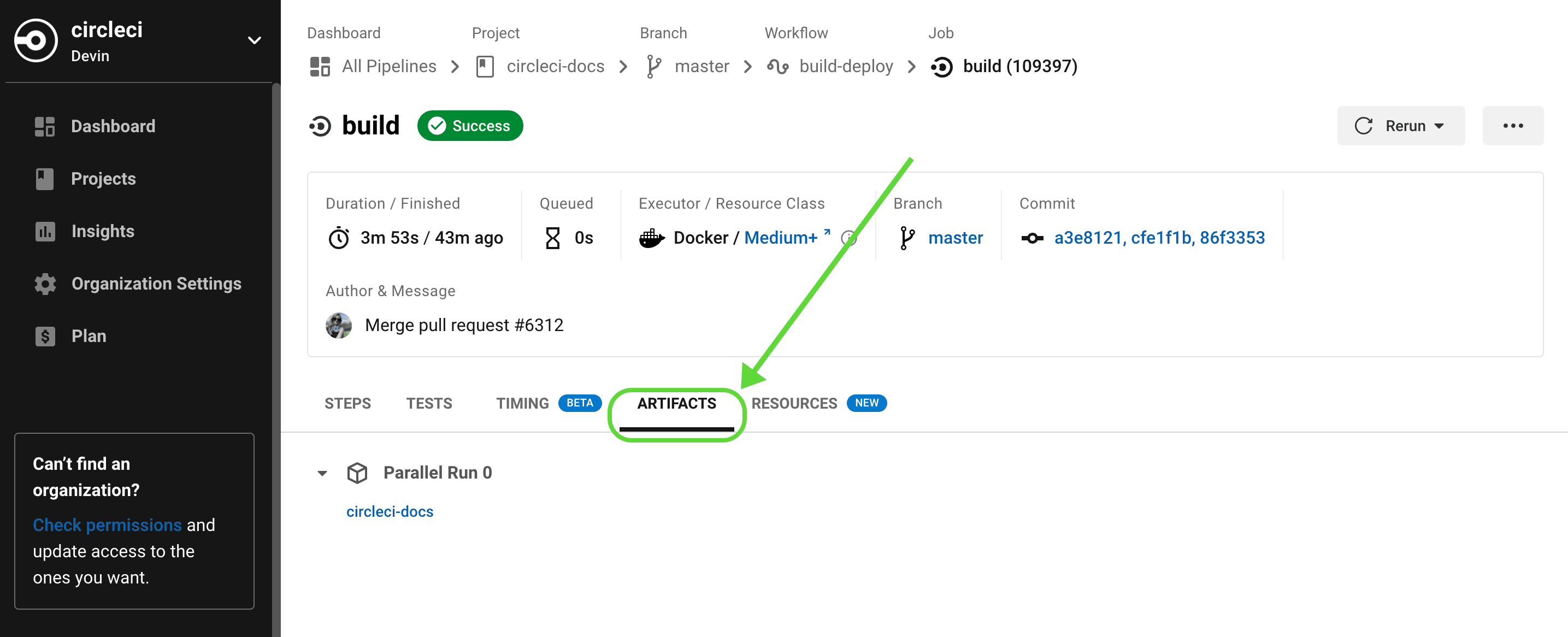
Here are a few examples to demonstrate configuring coverage libraries for different languages.
Ruby
Simplecov is a popular Ruby code coverage library. To get started, add the simplecov gem to your Gemfile
gem 'simplecov', require: false, group: :test
Start simplecov when your test suite starts. The example below demonstrates configuring simplecov for usage with Rails.
require 'simplecov' # << Require simplecov
SimpleCov.start 'rails' # << Start simplecov, using the "Rails" preset.
ENV['RAILS_ENV'] ||= 'test'
require_relative '../config/environment'
require 'rails/test_help'
class ActiveSupport::TestCase
# Setup all fixtures in test/fixtures/*.yml for all tests in alphabetical order.
fixtures :all
# Add more helper methods to be used by all tests here...
end
Now configure your .circleci/config.yml for uploading your coverage report.
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/ruby:3.0-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
environment:
RAILS_ENV: test
- image: cimg/postgres:14.0
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: circleci-demo-ruby
POSTGRES_DB: rails_blog
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: ""
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run:
name: Bundle Install
command: bundle check || bundle install
- run:
name: Wait for DB
command: dockerize -wait tcp://localhost:5432 -timeout 1m
- run:
name: Database setup
command: bin/rails db:schema:load --trace
- run:
name: Run Tests
command: bin/rails test
- store_artifacts:
path: coverage
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/ruby:3.0-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
environment:
RAILS_ENV: test
- image: cimg/postgres:14.0
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: circleci-demo-ruby
POSTGRES_DB: rails_blog
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: ""
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run:
name: Bundle Install
command: bundle check || bundle install
- run:
name: Wait for DB
command: dockerize -wait tcp://localhost:5432 -timeout 1m
- run:
name: Database setup
command: bin/rails db:schema:load --trace
- run:
name: Run Tests
command: bin/rails test
- store_artifacts:
path: coverage
# Legacy convenience images (i.e. images in the `circleci/` Docker namespace)
# will be deprecated starting Dec. 31, 2021. Next-gen convenience images with
# browser testing require the use of the CircleCI browser-tools orb, available
# with config version 2.1.
version: 2
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: circleci/ruby:2.5.3-node-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
environment:
RAILS_ENV: test
- image: cimg/postgres:9.6
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: circleci-demo-ruby
POSTGRES_DB: rails_blog
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: ""
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: Bundle Install
command: bundle check || bundle install
- run:
name: Wait for DB
command: dockerize -wait tcp://localhost:5432 -timeout 1m
- run:
name: Database setup
command: bin/rails db:schema:load --trace
- run:
name: Run Tests
command: bin/rails test
- store_artifacts:
path: coverage
The simplecov README has more details.
Python
Coverage.py is a popular library for generating Code Coverage Reports in python. To get started, install Coverage.py:
pip install coverage
# previously you might have run your python project like:
python my_program.py arg1 arg2
# now prefix "coverage" to your command.
coverage run my_program.py arg1 arg2
In this example, you can generate a coverage report with the following commands:
coverage run -m pytest
coverage report
coverage html # open htmlcov/index.html in a browser
The generated files will be found under htmlcov/, which can be uploaded in a store_artifacts step in your config:
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/python:3.10-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run:
name: Setup testing environment
command: |
pip install '.[test]' --user
echo $HOME
- run:
name: Run Tests
command: |
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage run -m pytest
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage report
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage html # open htmlcov/index.html in a browser
- store_artifacts:
path: htmlcov
workflows:
test-workflow:
jobs:
- build
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/python:3.10-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run:
name: Setup testing environment
command: |
pip install '.[test]' --user
echo $HOME
- run:
name: Run Tests
command: |
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage run -m pytest
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage report
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage html # open htmlcov/index.html in a browser
- store_artifacts:
path: htmlcov
workflows:
test-workflow:
jobs:
- build
# Legacy convenience images (i.e. images in the `circleci/` Docker namespace)
# will be deprecated starting Dec. 31, 2021. Next-gen convenience images with
# browser testing require the use of the CircleCI browser-tools orb, available
# with config version 2.1.
version: 2
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: circleci/python:3.7-node-browsers-legacy
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: Setup testing environment
command: |
pip install '.[test]' --user
echo $HOME
- run:
name: Run Tests
command: |
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage run -m pytest
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage report
$HOME/.local/bin/coverage html # open htmlcov/index.html in a browser
- store_artifacts:
path: htmlcov
workflows:
version: 2
workflow:
jobs:
- build
Java
JaCoCo is a popular library for Java code coverage. Below is an example pom.xml that includes JUnit and JaCoCo as part of the build system:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.foo</groupId>
<artifactId>DemoProject</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>DemoProject</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.6</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.6</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.8.3</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>prepare-agent</id>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>report</id>
<phase>prepare-package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>post-unit-test</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<!-- Sets the path to the file which contains the execution data. -->
<dataFile>target/jacoco.exec</dataFile>
<!-- Sets the output directory for the code coverage report. -->
<outputDirectory>target/my-reports</outputDirectory>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<systemPropertyVariables>
<jacoco-agent.destfile>target/jacoco.exec</jacoco-agent.destfile>
</systemPropertyVariables>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Running mvn test will include a code coverage report (an exec) file that is also converted to an html page, like many other coverage tools. The Pom file above writes to the target directory, which you can then store as an artifact in your CircleCI config.yml file.
Here is a minimal CI configuration to correspond with the above example:
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/openjdk:17.0-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run : mvn test
- store_artifacts:
path: target
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/openjdk:17.0-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run : mvn test
- store_artifacts:
path: target
# Legacy convenience images (i.e. images in the `circleci/` Docker namespace)
# will be deprecated starting Dec. 31, 2021. Next-gen convenience images with
# browser testing require the use of the CircleCI browser-tools orb, available
# with config version 2.1.
version: 2
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: circleci/openjdk:11.0-stretch-node-browsers-legacy
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- run : mvn test
- store_artifacts:
path: target
JavaScript
Istanbul is a popular library for generating code coverage reports for JavaScript projects. Another popular testing tool, Jest, uses Istanbul to generate reports. Consider this example:
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/node:17.2-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run: npm install
- run:
name: "Run Jest and Collect Coverage Reports"
command: jest --collectCoverage=true
- store_artifacts:
path: coverage
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/node:17.2-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run: npm install
- run:
name: "Run Jest and Collect Coverage Reports"
command: jest --collectCoverage=true
- store_artifacts:
path: coverage
# Legacy convenience images (i.e. images in the `circleci/` Docker namespace)
# will be deprecated starting Dec. 31, 2021. Next-gen convenience images with
# browser testing require the use of the CircleCI browser-tools orb, available
# with config version 2.1.
version: 2
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: circleci/node:14.17-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- run: npm install
- run:
name: "Run Jest and Collect Coverage Reports"
command: jest --collectCoverage=true
- store_artifacts:
path: coverage
PHP
PHPUnit is a popular testing framework for PHP. To generate code-coverage reports you may need to install PHP Xdebug if you are using an earlier version than PHP 5.6. Versions of PHP after 5.6 have access to a tool called phpdbg; you can generate a report using the command phpdbg -qrr vendor/bin/phpunit --coverage-html build/coverage-report
In the following basic .circleci/config.yml we upload the coverage reports in the store_artifacts step at the end of the config.
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/php:8.1-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run:
name: "Run tests"
command: phpdbg -qrr vendor/bin/phpunit --coverage-html build/coverage-report
environment:
XDEBUG_MODE: coverage
- store_artifacts:
path: build/coverage-report
version: 2.1
orbs:
browser-tools: circleci/browser-tools@1.2.3
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/php:8.1-browsers
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- browser-tools/install-browser-tools
- run:
name: "Run tests"
command: phpdbg -qrr vendor/bin/phpunit --coverage-html build/coverage-report
environment:
XDEBUG_MODE: coverage
- store_artifacts:
path: build/coverage-report
# Legacy convenience images (i.e. images in the `circleci/` Docker namespace)
# will be deprecated starting Dec. 31, 2021. Next-gen convenience images with
# browser testing require the use of the CircleCI browser-tools orb, available
# with config version 2.1.
version: 2
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: circleci/php:7-fpm-browsers-legacy
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: "Run tests"
command: phpdbg -qrr vendor/bin/phpunit --coverage-html build/coverage-report
environment:
XDEBUG_MODE: coverage
- store_artifacts:
path: build/coverage-report
Golang
Go has built-in functionality for generating code coverage reports. To generate reports, add the flag -coverprofile=c.out. This will generate a coverage report which can be converted to html via go tool.
go test -cover -coverprofile=c.out
go tool cover -html=c.out -o coverage.html
An example .circleci/config.yml:
version: 2.1
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: cimg/go:1.16
auth:
username: mydockerhub-user
password: $DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD # context / project UI env-var reference
steps:
- checkout
- run: go build
- run:
name: "Create a temp directory for artifacts"
command: |
mkdir -p /tmp/artifacts
- run:
command: |
go test -coverprofile=c.out
go tool cover -html=c.out -o coverage.html
mv coverage.html /tmp/artifacts
- store_artifacts:
path: /tmp/artifacts
Using a code coverage service
Codecov
Codecov has an orb to help simplify the process of uploading your coverage reports.
Note: The Codecov orb is a Partner orb. You or your organization admin will need to opt in to using uncertified orbs in order to use it. This setting is available at Organization Settings > Security in the CircleCI web app.
version: 2.1
orbs:
codecov: codecov/codecov@1.0.2
jobs:
build:
steps:
- codecov/upload:
file:
Read more about Codecov’s orb in their guest blog post.
Coveralls
If you’re a Coveralls customer, follow their guide to set up your coverage stats. You’ll need to add COVERALLS_REPO_TOKEN to your CircleCI environment variables.
Coveralls will automatically handle the merging of coverage stats in concurrent jobs.
Help make this document better
This guide, as well as the rest of our docs, are open source and available on GitHub. We welcome your contributions.
- Suggest an edit to this page (please read the contributing guide first).
- To report a problem in the documentation, or to submit feedback and comments, please open an issue on GitHub.
- CircleCI is always seeking ways to improve your experience with our platform. If you would like to share feedback, please join our research community.
Need support?
Our support engineers are available to help with service issues, billing, or account related questions, and can help troubleshoot build configurations. Contact our support engineers by opening a ticket.
You can also visit our support site to find support articles, community forums, and training resources.

CircleCI Documentation by CircleCI is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



